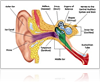
Considered to be the most complex part of the ear, the cochlea helps us distinguish the sounds around us. While the cochlea is small, it plays a vital role in our ability to hear and perceive the world around us. Located in the inner ear, the cochlea receives sound waves and transforms them into nerve impulses. The nerve impulses get sent to the brain, where they are then translated into sound.
It’s no surprise that the cochlea is the most complex part of the ear. To better appreciate this amazing organ, check out our list of cochlear facts.
1. The cochlea is located in the inner ear.
2. The toughest bone in the human body is the petrosal bone, and it protects the inner ear and the cochlea.
3. The cochlea is a Greek name that means snail. Which is very fitting, considering the cochlea looks just like a snail shell!
4. Approximately 24,000 hair fibers can be found within the cochlea. These hair cells are necessary for hearing.
5. The cochlea would be about 31.5mm long if it were to be “unrolled.”
6. The cochlea is the first organ to develop completely and is formed 4 ½ months into a pregnancy.
7. Hearing impairment will occur if any of the hair cells in the cochlea become damaged.
8. Different sounds will move the hair cells different ways. The brain uses this to distinguish one sound from another.
9. The cochlea is tiny and pea-sized, but yet packs a powerful punch!
10. The cochlea is sensitive and does not have the ability to heal itself. Loud noises, toxins, trauma, drugs, disease, and the aging process is often the cause of cochlear damage.
11. Within the cochlea is everything we need to turn sound waves into perceivable sounds.
12. The cochlea is filled with fluid, and it is this fluid that moves sensory hairs and translates the vibrations into nerve impulses.
13. Cochlear implants can directly stimulate the auditory nerve. By using cochlear implants, damaged hair cells can be bypassed.